GPA Grading Scale – How Letter Grades Convert Into GPA?
Trying to figure out how your letter grades actually impact your college GPA? It’s not as simple as averaging percentages, especially when credit hours, course difficulty, and grading systems all come into play.
Whether you’re aiming for honors, applying for scholarships, or just tracking your academic progress, understanding how the GPA grading scale works is a crucial step.
In this guide, I’ll break it all down, from how your A’s and B’s translate into grade points to how schools calculate weighted vs. unweighted GPAs.
This isn’t just about numbers. It’s about making smart academic decisions with clarity. You’ll also find helpful visuals, real examples, and the most common GPA systems used in the U.S.
Let’s start by defining what the GPA scale actually is, and why it’s used.
If you want to calculate your semester or cumulative GPA, use our FREE, online, College GPA Calculator, built by a student, for students.
What Is the GPA Grading Scale?
Your GPA, or Grade Point Average, is the numerical reflection of your academic performance. It tells schools, employers, and scholarship boards how you’ve done, but not in letter grades or percentages. Instead, it’s a weighted average of the grade points you’ve earned per credit hour.
In most U.S. schools, GPA grading scale 4.0 is used, where:
- A = 4.0
- B = 3.0
- C = 2.0
- D = 1.0
- F = 0.0
It looks simple on the surface. But when you factor in credit hours, honors classes, and plus/minus grades, that’s where things get complex.
So, how is GPA different from just using letter grades or percentages? Here’s how:
- Percentages are raw scores (like 92%)
- Letter grades categorize performance (like A-)
- GPA turns those categories into a scale that can be averaged across semesters
That makes GPA a universal metric, a way to compare academic strength regardless of school, course load, or curriculum.
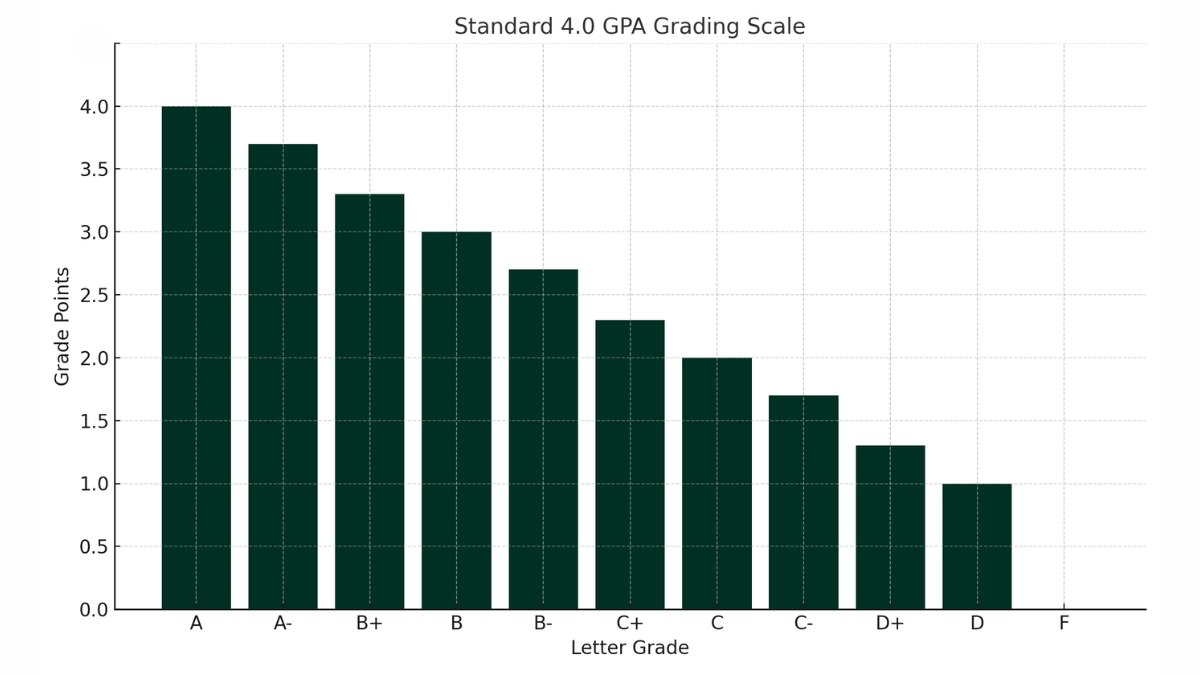
Letter Grades To GPA: A Quick Conversion Guide
Every letter grade corresponds to a number on the GPA scale. But here’s the catch: not every school uses the exact same values. Still, the chart below reflects the standard conversion used by most colleges.
| Letter Grade | GPA Value |
|---|---|
| A | 4.0 |
| A– | 3.7 |
| B+ | 3.3 |
| B | 3.0 |
| B– | 2.7 |
| C+ | 2.3 |
| C | 2.0 |
| C– | 1.7 |
| D+ | 1.3 |
| D | 1.0 |
| F | 0.0 |
So, if you got an A in a 3-credit course, that’s 3 x 4.0 = 12 quality points. If you got a B+ in a 4-credit course, that’s 4 x 3.3 = 13.2 quality points.
Some schools don’t use plus or minus grades at all. Others may assign different values to an A+ (sometimes 4.3). That’s why it’s important to check your school’s GPA policy.
Still, most colleges, especially when evaluating transcripts or transfer credits, normalize everything to the standard 4.0 scale.
The Difference Between Weighted and Unweighted GPA

Not all classes carry the same weight, and not all GPAs are calculated equally.
An unweighted GPA is the standard 4.0 scale we just saw. It treats all courses the same, whether it’s basic English or AP Chemistry. A 4.0 is the highest you can get, even in advanced or honors classes.
A weighted GPA gives extra points for more rigorous coursework, like:
- Honors classes
- Advanced Placement (AP) courses)
- International Baccalaureate (IB) programs
So instead of maxing out at 4.0, a weighted GPA might reach 4.5 or even 5.0. For example:
- A in a regular class = 4.0
- A in an honors class = 4.5
- A in an AP class = 5.0
Let’s say you earn a B in AP Biology. That’s still worth more than a B in regular Biology. This scale rewards students for challenging themselves academically.
Here’s why this matters: colleges often look at both. The weighted GPA shows your academic rigor. The unweighted GPA helps compare students fairly across different high schools.
Some schools report only one type. Others give both. And yes, it can impact your class rank, honors designation, and eligibility for programs.
Common GPA Scales In The U.S.
While the 4.0 GPA scale is the most widely used, it’s not the only one. Different schools and districts adopt different grading systems, and that can create confusion when applying to colleges, scholarships, or internships.
Let’s break down the three most common GPA scales:
1. The Standard 4.0 Scale (Unweighted)
- Most U.S. colleges and high schools use this scale.
- It caps at 4.0 (A = 4.0, B = 3.0, etc.).
- No extra weight is given to advanced courses.
It’s simple, fair, and universal, which is why admissions committees rely on it to compare students across schools.
2. The Weighted 5.0 Scale
- Used in schools that want to reward course difficulty.
- Honors, AP, or IB classes can push GPA up to 5.0.
- A student might earn a 4.5 GPA if they take all advanced classes and perform well.
This scale highlights academic rigor. Students competing for top universities often submit both weighted and unweighted GPAs to show the full picture.
3. The 100-Point Scale
- Used by some schools in place of letter grades.
- A student may get an 88%, 94%, or 79% on a course.
- These percentages are later converted to a GPA (e.g., 90–100% = A = 4.0).
Conversion from this scale varies; some schools might use strict cutoffs, while others may round. That’s why GPA conversion charts are essential when translating your grades for college applications.
What About Plus and Minus Grades?
Some schools apply pluses and minuses to your letter grades, which slightly adjust your GPA:
- A– = 3.7 instead of 4.0
- B+ = 3.3 instead of 3.0
Others might ignore them altogether and treat an A– or A+ the same as an A. It’s important to know how your school handles this, as it can impact your GPA more than you think.
Why Does GPA Matter For Students?

Your GPA isn’t just a number. It’s a critical indicator of academic performance, and it plays a significant role in shaping your academic journey and future career.
Whether you’re applying for financial aid, transferring schools, or planning for grad school, understanding how your GPA is calculated and what scale it’s based on is essential.
Here’s how your GPA can influence your future in real, tangible ways:
1. Scholarships and Financial Aid
Most scholarships, especially merit-based ones, come with GPA requirements. These cutoffs can range from a minimum of 2.5 for general eligibility to 3.5 or higher for prestigious or fully funded programs. If your GPA doesn’t meet the threshold, your application may not even be reviewed.
And it doesn’t end there. Many scholarships and financial aid packages are renewable, meaning you must maintain a certain GPA every semester or year to continue receiving them.
Whether it’s a government grant, private scholarship, or institutional aid, your GPA and performance directly impact how much support you get.
In short, a high GPA could mean graduating with less student debt, or even none at all.
2. Graduate School Applications
When you’re applying to medical school, law school, business school, or any graduate-level program, your undergraduate GPA is one of the first things admissions committees evaluate.
Why? Because your GPA reflects academic consistency. While test scores like the GRE, MCAT, or LSAT offer a snapshot of your aptitude, GPA shows your long-term work ethic, your ability to manage course loads, and your commitment over time.
In competitive programs, even a difference of 0.2 on your GPA can be the reason you’re accepted or rejected. If your test scores aren’t ideal, a strong GPA can offset them and help you stand out in a field of equally qualified applicants.
3. Transfer Applications
Thinking of transferring from a community college to a four-year university? Or switching from one university to another?
Your cumulative GPA becomes your academic résumé. Most transfer programs have minimum GPA requirements, usually around 2.5 to 3.0, but competitive programs can ask for 3.5 or higher.
Admissions teams assess your GPA to ensure you’ve demonstrated academic growth and course rigor, especially if you’re switching into a demanding program like engineering, computer science, or business.
If your GPA doesn’t meet the standard, you might lose transfer credits or face conditional admission, delaying your graduation timeline.
4. Class Rank and Academic Honors
Your GPA determines your class rank, a key factor in earning honors like:
- Dean’s List
- Honor Roll
- Summa Cum Laude, Magna Cum Laude
- Valedictorian or Salutatorian titles
These honors don’t just make your academic record look impressive; they can also unlock exclusive scholarships, research opportunities, and internship offers.
Plus, academic honors are often included on your transcript, making a lasting impression when applying to competitive programs or jobs.
5. Job Applications and Internships
Yes, many employers do look at your GPA, especially if you’re applying for:
- Entry-level jobs
- Internships
- Corporate training programs
- Roles in competitive fields like tech, finance, consulting, or law
In fact, some job listings explicitly state a minimum GPA requirement (often 3.0 or higher). A strong GPA signals more than academic success. It suggests discipline, responsibility, consistency, and time management, all qualities employers look for.
Even if GPA isn’t the main hiring factor, it can enhance your resume, especially when you lack real-world experience. It’s one more way to prove you’re serious, capable, and prepared.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do I know what scale my college uses?
Check your school’s course catalog or registrar’s website. You can also ask your advisor. Most colleges use a 4.0 or 5.0 scale.
Does a 3.5 GPA mean 85% or a B+?
Not exactly. A 3.5 GPA roughly equals a B+ or 85%, but GPA is based on grade points and credit weight, not just percentages.
Is GPA calculated differently in college than high school?
Yes. High schools often use weighted GPAs for AP/honors. Colleges usually calculate unweighted GPAs based on credit hours and letter grades.
Final Thoughts On GPA Grading Scale
Your GPA grading scale does more than measure performance—it shapes how you plan, apply, and progress. When you know how each grade impacts your average, you gain the clarity to set goals, adjust efforts, and stay in control of your academic path.
This guide aimed to simplify what often feels like a confusing system. And now that you understand how it works, from letter grade conversions to weighted and unweighted scales, you’re one step closer to making smarter academic decisions.
Your GPA doesn’t define your worth, but it can open or close important doors. So take ownership, stay informed, and use tools like this one to stay on track.
You’ve got this.
Refrences
- GRE Test – ETS
- Magna Cum Laude – Investopedia
